Environmental impacts of plastic injection moulding
The green movement is increasingly influencing all sectors, urging businesses to reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to environmental sustainability. While plastics are often criticised for their environmental impact, the plastic moulding industry can be both economically and environmentally beneficial when implemented responsibly.
What is plastic injection moulding?
Plastic injection moulding is essential for mass-producing thermoplastic components with high precision and minimal finishing. Modern machines are typically universal, capable of handling various moulds within specified limits. This process excels in producing complex geometries, offering a competitive edge over other methods. While the initial equipment cost is high, per-unit costs decrease as production volume rises.
Micro moulding is a highly specialised technique in which micro-structured steel or aluminium moulds are CNC and EDM machined to micron or even sub-micron scale tolerances, and the final moulded object could weigh a fraction of a gram or its tiny features. The fundamental distinction between micro moulding and standard moulding technologies is the size of the shot and the precision of the injection equipment. Micro-moulding machines can inject fractions of a gram with great precision because they offer better resolution feed choices, resulting in equal pressure distribution inside the cavity. Micro injection moulding also employs tiny moulds with highly precise core, cavities and features within.
Environmental impacts of plastic injection moulding
The environmental effects of plastic injection moulding might vary based on the materials used, the method itself and the types of waste created.
Material
Plastic is the primary material in injection moulding, and its environmental impacts are considerable, including greenhouse gas emissions and plastic waste in rivers and oceans. Plastic production is energy-intensive, releasing pollutants such as VOCs, sulphur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. In the UK, plastic consumption generates 26 Mt CO2e annually, with 80% of emissions from production, both domestically and internationally. Plastics, sourced from fossil fuels, account for 17% of emissions, while recycling and disposal contribute just 2.3%. Furthermore, plastic packaging often faces recycling challenges. Changing market demands and increased customer awareness are shaping the injection moulding industry.
Customers are concerned about reducing their carbon footprint, and more producers have been able to greatly expand the usage of post-consumer recycled plastics in LDPE-manufactured components. Since April 2021, virtually all LDPE goods manufactured at the UK site have been made with at least 40% recycled polymers, with no loss in quality or performance.
Metals and other materials used in injection moulding can have significant environmental impacts. The production of metals like aluminium and steel is energy-intensive and polluting. While using recycled materials, such as plastics, can reduce environmental impact, it may not be viable for medical components.
Energy
The plastic injection moulding process can impact the environment due to its high energy consumption, contributing to air pollution and global warming. Energy efficiency varies based on factors like melt temperature, component weight, cycle time, and machine size. For instance, 0.3 kWh/kg is efficient for thin-walled components, while 0.6 kWh/kg suits thicker parts (H. Schut, 2015). Recent engineering improvements have reduced energy use by 20%-50% in the last decade (H. Schut, 2015). Energy consumption can be estimated using an injection moulding calculator.
Electric injection moulding machines improve repeatability, reduce noise, shorten injection times, and increase energy efficiency, thanks to dynamic servo motors with exceptional acceleration. These machines only consume energy during operation, making them more energy-efficient than traditional hydraulic systems.
In hydraulic machines, the base load (energy used while idling) can account for over 75% of total energy consumption, while in all-electric and hybrid machines, it is typically 10-20%, primarily for barrel heating (Mobil). A high base load may indicate over-sizing of equipment.
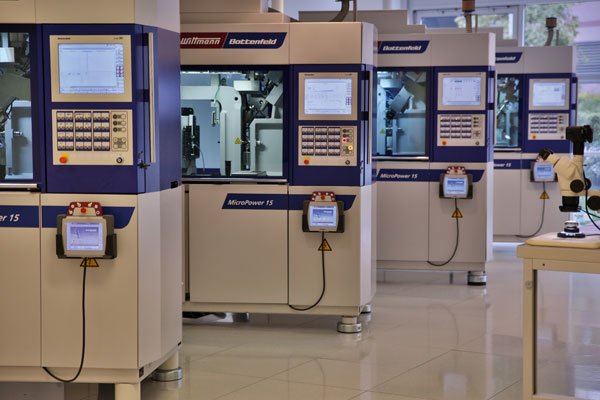
To improve environmental performance, injection moulding companies should prioritise renewable energy, conduct regular maintenance, and adopt technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT). For instance, Wittmann Battenfeld’s SmartPower machines are six times more energy-efficient and cost-effective than models from the 1990s. At Micro Systems, we optimise energy use through advanced machinery, frequent maintenance, and continuous improvement of our resources.
Current all-electric moulding machines use energy ratios that are equivalent to those of previous hydraulic machines, but overall energy usage is around 50% less (Photo: Micro Systems)
Waste
Plastic injection moulding generates considerable plastic waste, which can be challenging to recycle. This scrap often ends up in landfills, where it can take centuries to decompose, releasing harmful compounds that contaminate the air, water, and soil.
One common waste product is plastic sprues, the remnants of material left after the moulding process. These can be locally recycled. At Micro Systems, we collaborate with a local recycling firm to re-granulate our plastic waste, including sprues. This not only benefits the environment but also helps reduce our carbon footprint by supporting local businesses.
Furthermore, manufacturers can minimise waste by optimising variables such as volume, temperature, design, and injection pressure. By ensuring the finished product is flawless, minimal virgin plastic is wasted. Effective mould design can also eliminate flash and sprues, further reducing waste generation.
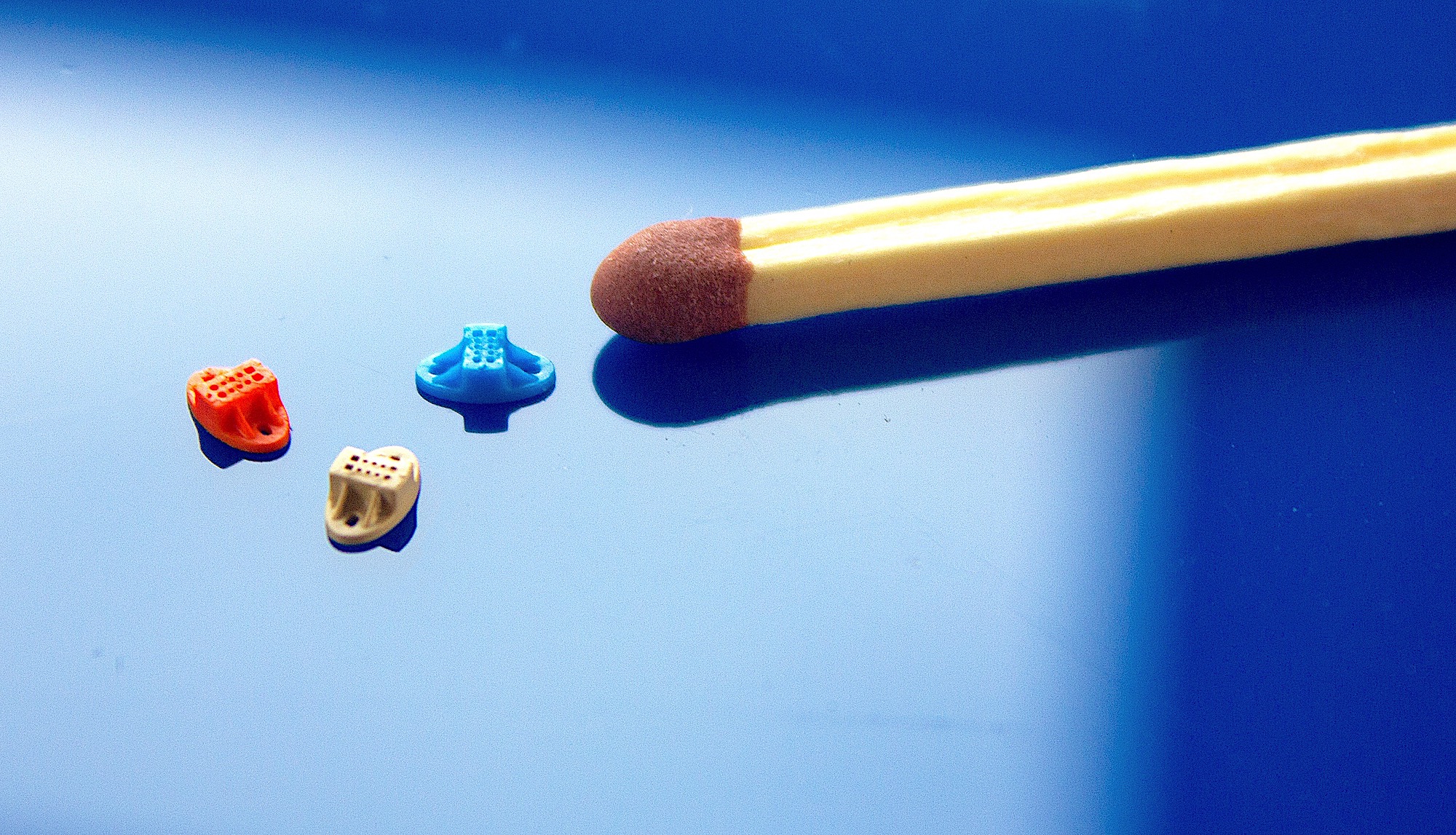
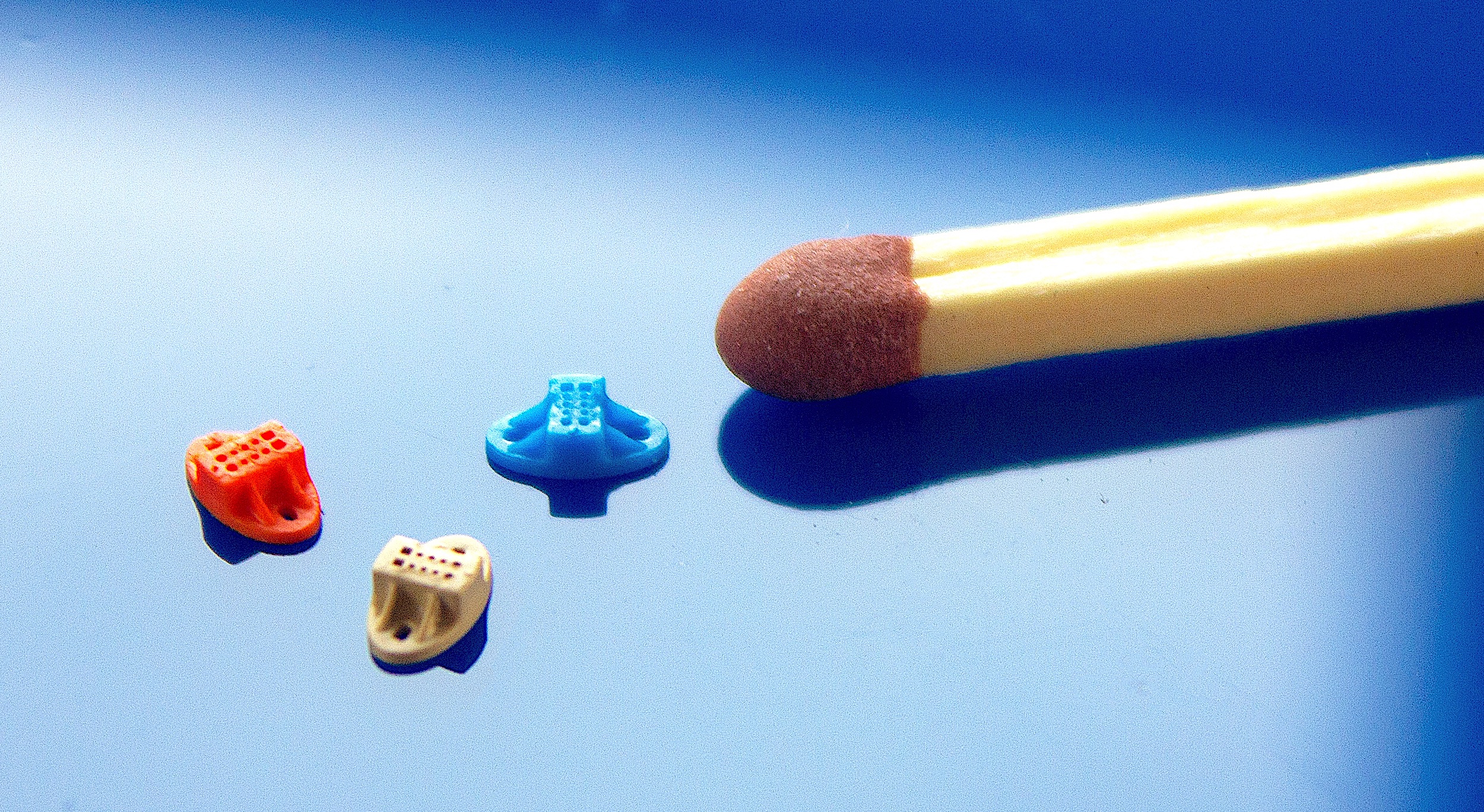
Micro injection moulded parts for medical uses (Photo: Micro Systems)
With the development of technology, together with extensive expertise and knowledge, injection moulding manufacturers are getting more and more environmentally friendly, producing millions of parts a year at a lower carbon footprint. At Micro Systems, we are committed to operating with responsibility at all stages throughout our production process, such that we can fully support our customers on their journey towards sustainability in business.
Check out our 2022 CSR Report here!
References:
H. Schut, J. (no date) Plastics Engineering – March 2015, Eco-Molding: More Power for Less Energy. Available at: http://read.nxtbook.com/wiley/plasticsengineering/march2015/coverstory_ecomolding.html (Accessed: 19 May 2023).
Mobil (ed.) (no date) An Energy Saving Guide for Plastic Injection Molding Machines. Applied Market Information in association with Tangram Technology.

Micro Systems is a well-established supplier in micro plastic injection moulding, offering considerable experiences in micro moulds, the design, manufacture, FAT and validation of multi cavity valve gate high volume injection moulds for the medical, pharmaceutical and ophthalmic markets. In our local community and in injection moulding across the world, we seek to be a paradigm for sustainability in design and manufacture. For more information, please Contact us or visit our website.