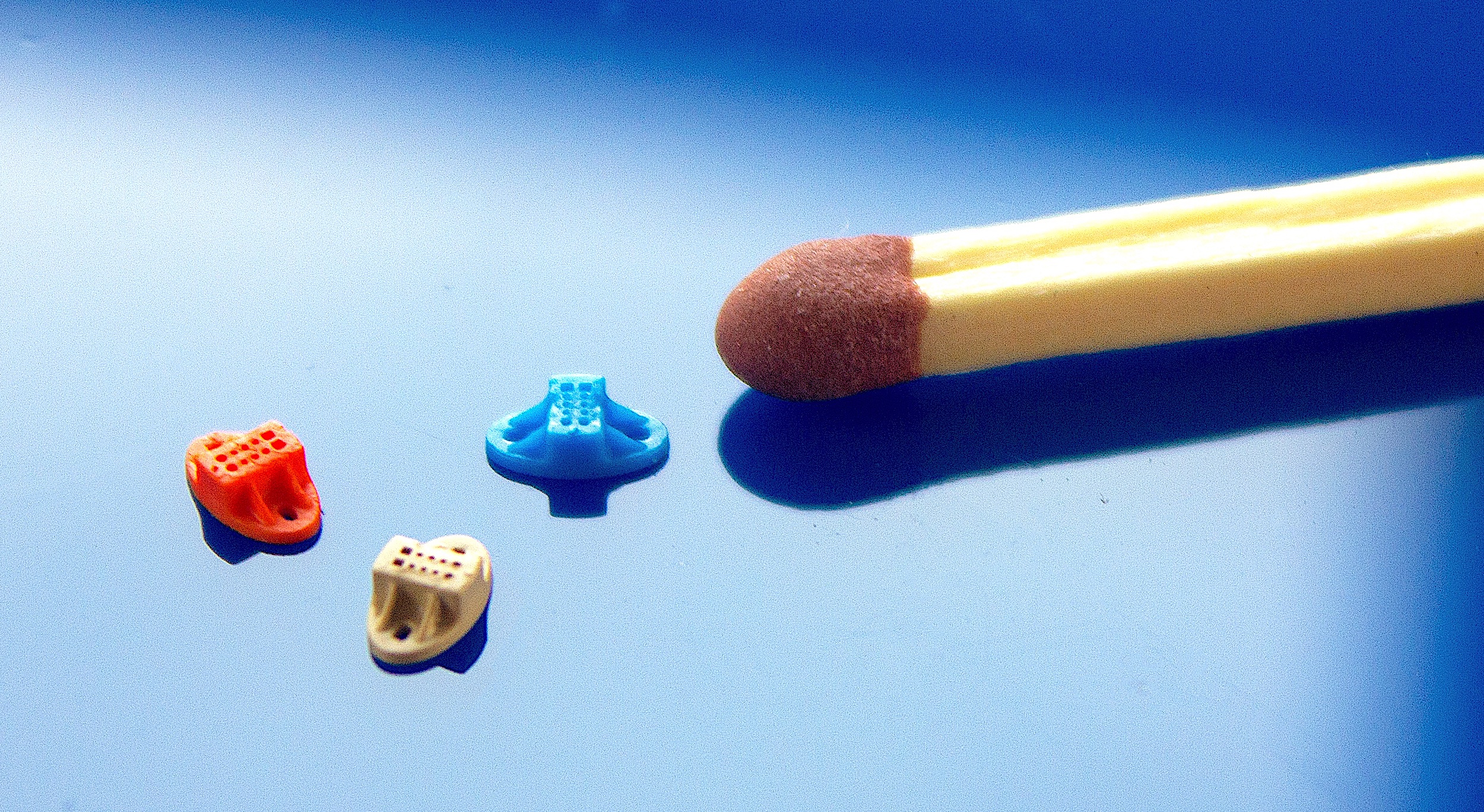
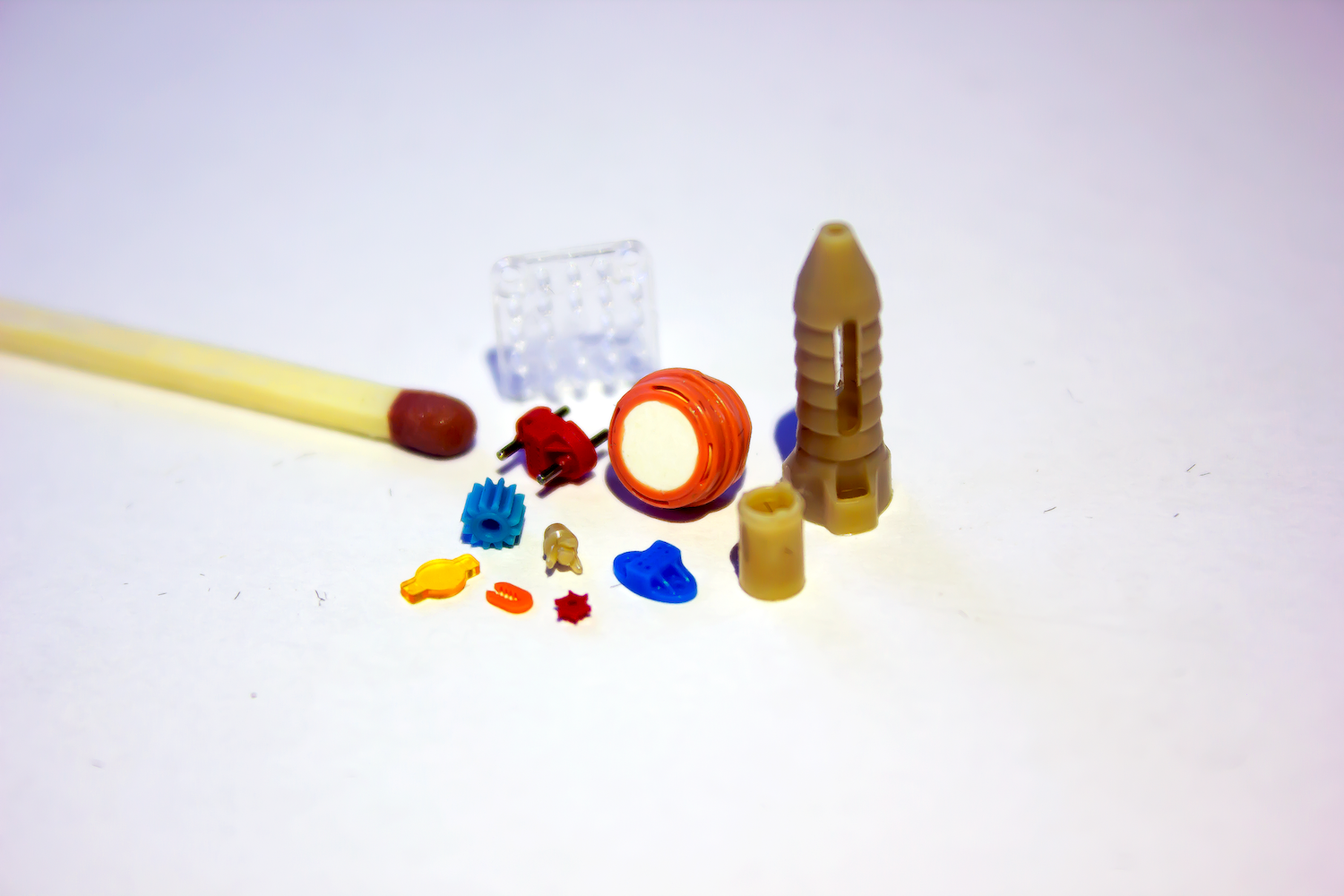
What is ISO 13485?
Within the medical device industry, it is crucial for manufacturers to be able to supply products with the highest level of safety and quality, demonstrating excellent quality management processes with best practices in every step. ISO 13485 is developed as an internationally agreed standard for the quality management system just for the medical device industry.
What is ISO 13485?
According to ISO 13485:2016, an organisation must be able to supply medical devices and related services that consistently fulfil the demands of the customer and any applicable regulatory requirements. ISO defines medical devices to be a product that is designed for use in the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of illnesses or other medical disorders. Examples could include instruments, machines, implants, and in vitro reagents.
A medical device’s design and development, manufacture, storage and distribution, installation or servicing, as well as the design and development or supply of related activities (such as technical assistance), are all activities that medical device manufacturers may be involved in at one or more phases of the life cycle. Suppliers and other outside parties that deliver goods to these organisations, including services connected to their quality management systems, are also permitted to adopt this ISO certification.
Except as specifically indicated, the requirements of ISO 13485:2016 apply to all organisations, regardless of size or kind. Wherever regulations are listed as being applicable to medical equipment, they also apply to related services provided by the organisation. ISO 13485 addresses Quality Control, Risk Management, Legal compliance, Operational efficiency, Ability to trace and recall products and devices, and Process and product improvement.
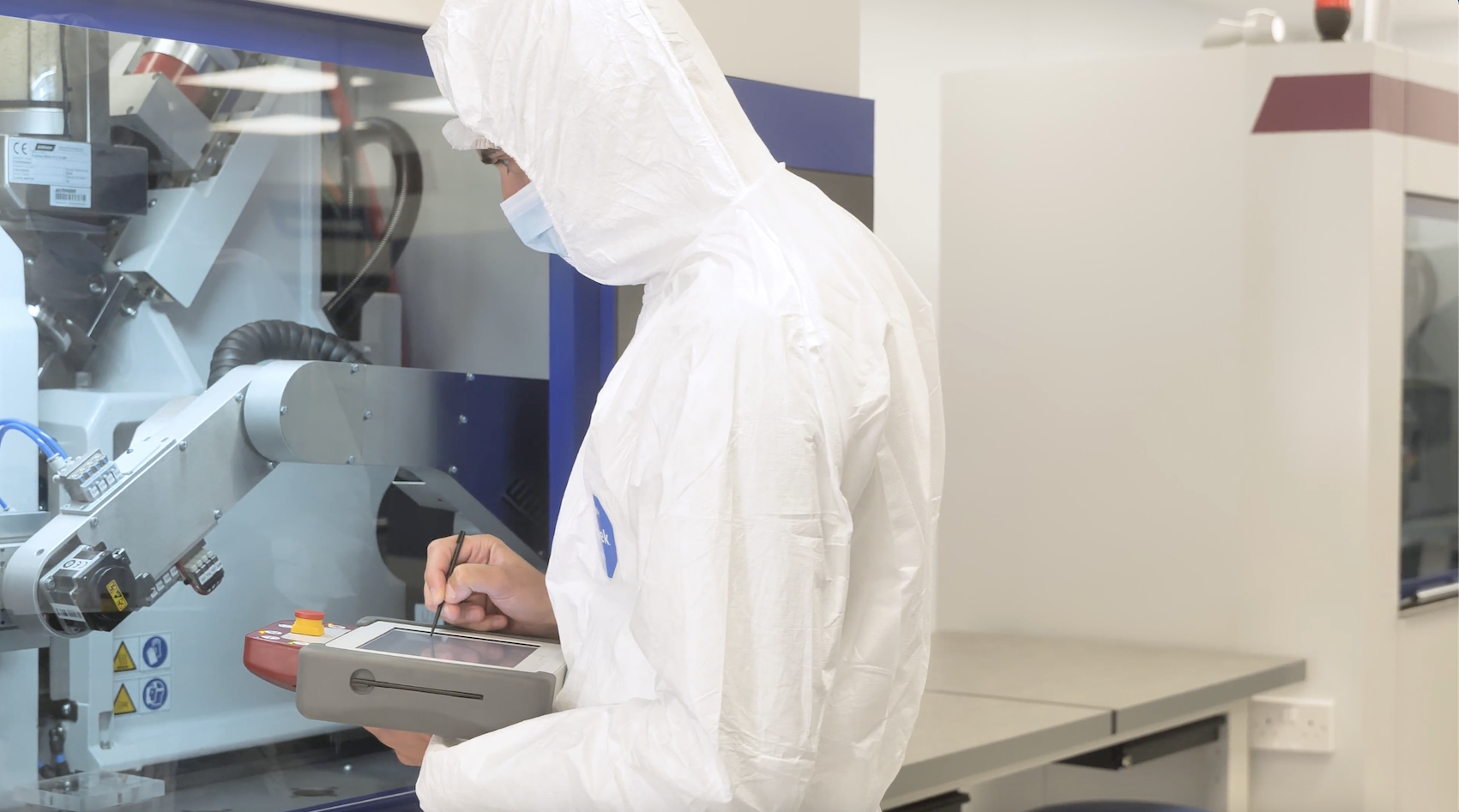

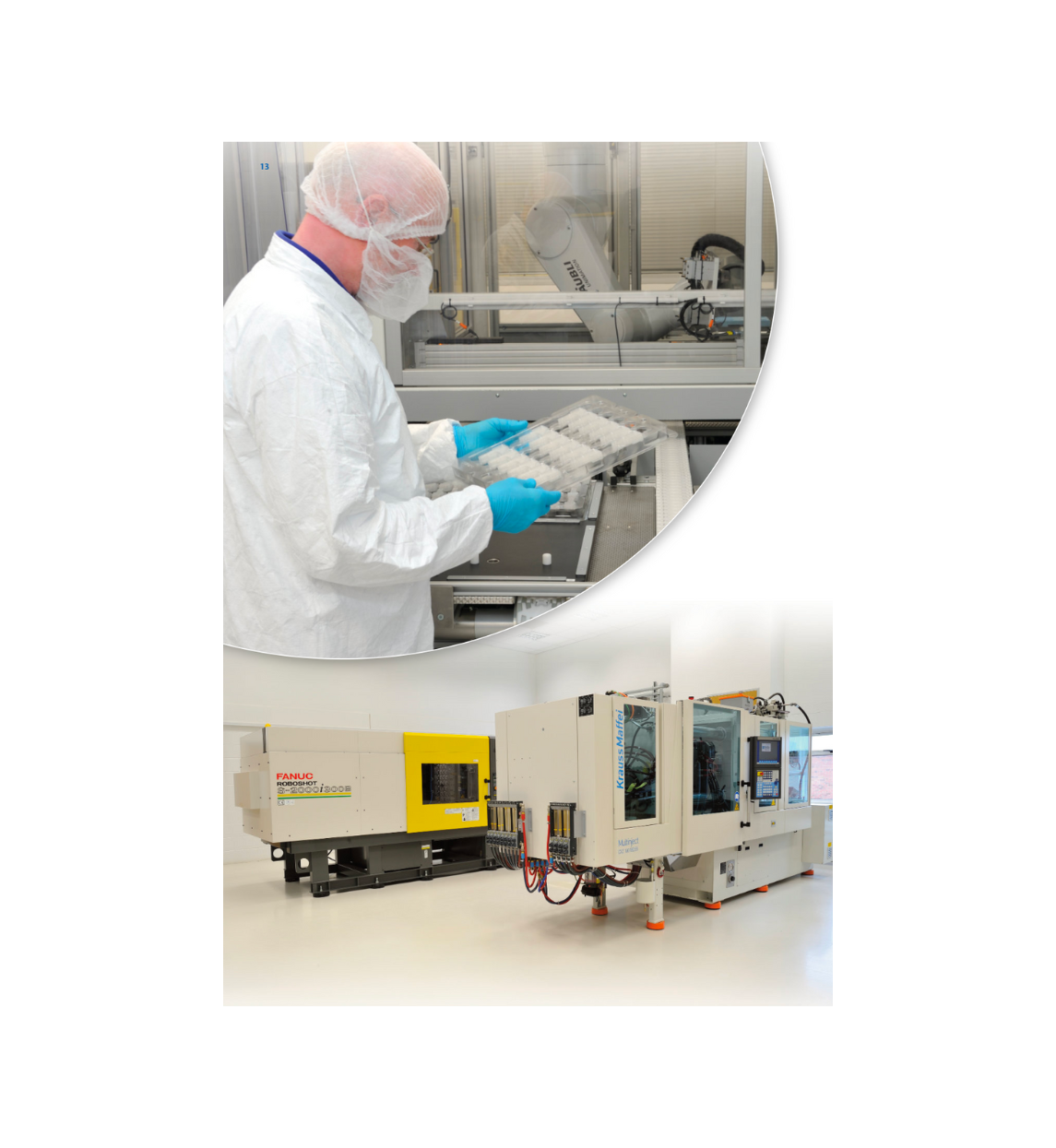
All steps throughout the processes at Micro Systems strictly follow the highly-set standards (Photo: Micro Systems)
What are the benefits of ISO 13485?
Being ISO 13485 accredited brings a number of benefits to the organisation in various aspects.
Firstly, this medical-related ISO allows organisations to increase the ability to contract with larger clients and expand their potential markets. Working with suppliers that have an ISO 13485 certification is prioritised by many sizable medical device companies, especially when they have to take the responsibility for making sure that their subcontractors also follow ISO 13485 standards. The standard also serves as the initial step towards regulatory clearance in important markets like the European Union and Canada, as well as serving to convince potential customers of the high calibre of the product.
Secondly, having ISO 13485 certification shows the business’s dedication to high quality and outstanding standards. Obtaining a quality management accreditation shows clients and authorities that the business prioritises quality, which is significantly important in the field of medical devices. This will hence lead to higher customer satisfaction and trust, and potentially a longer business relationship in the future.
Internally, the efficient processes promoted by ISO 13485 guarantee seamless operations across the organisation. By standardising these processes, organisations may minimise duplications, cut down on mistakes, and maximise resource allocation. A focus on documentation, traceability, and risk management in the ISO 13485 standard also guarantees that the procedures and controls required to satisfy regulatory requirements are in place, hence, organisations can pass regulatory body inspections and audits more successfully if they continue to adhere to the standards. The standard documentation also makes it easier for employees to get the information when required, as a result, the time and cost involved in product development might be decreased with the correct information at hand. Through ISO 13485, creating a centralised knowledge base via the documentation of the processes related to their medical devices might also assist organisations in identifying issues, enhancing their offerings, and streamlining their production procedures.
Who should use ISO 13485?
ISO 13485 specifies quality management, indicating that a wide range of businesses in the supply chain for pharmaceuticals and medical devices could follow this standard. Companies that adhere to this standard could include:
- Medical device manufacturers;
- Suppliers of goods or raw materials to manufacturers that make medical devices;
- Organisations for quality control that work with producers of medical devices;
- Organisations that assist manufacturers of medical devices;
- Manufacturers of sterile medical equipment;
- Suppliers of surgical medical equipment.
Being certified as ISO 13485 compliant isn’t always required as it is optional, the standard serves as the foundation for the medical device regulations in several nations. For example, in order to have a medical device approved in Europe, one must first obtain ISO 9001 or ISO 13485 certification. Furthermore, the regulatory frameworks of several nations now include the criteria found in ISO 13485. It is used by regulators in Australia, Canada, the United States, the European Union, and Japan.
What is the difference between ISO 13485 and ISO 9001?

ISO 9001 can be utilised regardless of their industry, every organisation, no matter how big or little. In actuality, more than a million businesses and organisations in more than 170 nations have received ISO 9001 certification. This standard is founded on several quality management principles, such as a strong customer focus, top management involvement and motivation, the process method, and continuous improvement. The quality management principles of ISO provide a more thorough explanation of these ideas. Utilising ISO 9001 contributes to ensuring that clients receive dependable, high-quality goods and services, which has several positive effects for businesses.
There are few significant similarities between ISO 9001 and ISO 13485. Firstly, both standards help assisting organisations to establish a quality management system, with a significant focus on risk mitigation and assessment, and the realisation of quality products through understanding their customers. Furthermore, deming cycles (Plan-Do-Check-Act) are utilised by both ISO 9001 and ISO 13485. The two standards also place a strong emphasis on worker proficiency and quality infrastructure.
The main difference between ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 is that the latter is specifically used for medical device products, with unique sections and guidelines for the industry. The latter also focuses on meeting customer requirements rather than on subjective customer satisfaction measures. There are also other requirements regarding regulatory reporting, advisory notices and recalls.
Regarding Management Responsibility, while ISO 13485 mandates that a medical device maker choose a single individual from the management to be accountable for QMS, ISO 9001 permits organisations to disperse the duties for quality control without being connected to specific managers. ISO 13485 also focuses more on maintaining the effectiveness of the quality management system, rather than the continuous improvement as in ISO 9001.
Regarding Documentation Control, ISO 13485 is more demanding than ISO 9001 since it calls for the inclusion of regulatory documents, including full product specifications, descriptions of production processes, and instructions for installation and maintenance, in the system documentation.
Regarding Product Realisation, design and development remain crucial steps in this ISO accreditation, however, ISO 9001:2015 has changed to the definition of operational procedures for product delivery. The requirements of the client are prioritised over the documentation of the design and development in ISO 9001:2015.
Regarding Risk Management, ISO 13485 focuses on the creation of risk management paperwork and mandates that a producer of medical devices keep track of the risk management procedure throughout the medical device manufacturing, including the design and production stages. Additionally, the standard requires medical device manufacturers to examine customer complaints and set up post-sale oversight of the product’s adherence to the stated quality.
Regarding Resource Management, ISO 13485 also requires that developers and manufacturers of medical devices have the required mechanisms to record and manage industry-specific criteria, such as clothing cleanliness, temporary working circumstances and controls for contaminated products.
Micro Systems is accredited with both ISO 9001 and ISO 13485. Our on-site injection moulding facility Optimold is also accredited with ISO 13485. We are capable of taking on your most challenging medical device projects, from designing and manufacturing medical moulds to producing the final medical moulded parts, all within our ISO-certified clean rooms in the UK.
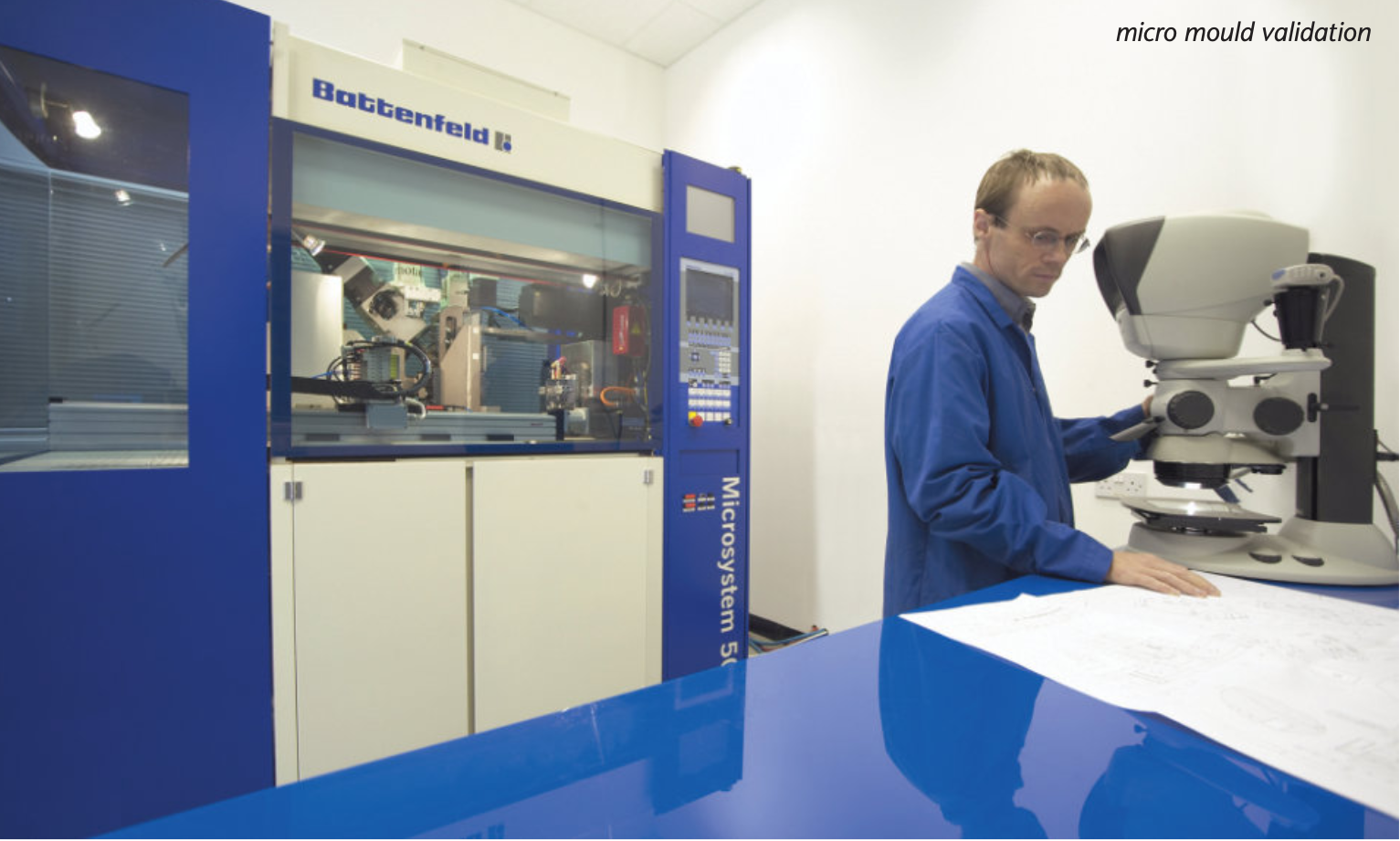

Micro Systems’s vast know-how in design, ultra-precision micro machining capabilities and expert knowledge in micro moulding technology allow us to manufacture advanced microfluidic moulds with tolerance as low as +/-0.001mm, with integrated optics. We have a dedicated micro moulding facility, and have ISO13485 and ISO9001 certifications. For more information, please Contact us or visit our website.